Create a free profile to get unlimited access to exclusive videos, sweepstakes, and more!
KABOOM! Nearby Galaxy M82 Hosts a New Supernova!
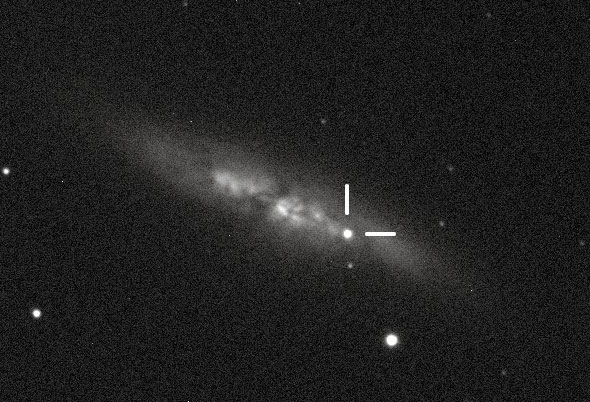

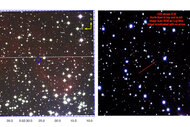
I woke up to some great science news: A supernova has gone off in the nearby galaxy M82!
This is terribly exciting for astronomers. M82 is pretty close as galaxies go, less than 12 million light years away. That means we have an excellent view of one of the biggest explosions in the Universe, and weâll be able to study it in great detail!
The supernova has the preliminary designation of PSN J09554214+6940260. I know, thatâs awfulâitâs based on the starâs coordinatesâbut itâll get a name soon enough thatâll be easier on the eyes and brain.
And just to get this out of the way, weâre in no danger from this explosion. Itâs far too far away. Also, you wonât be able to just go outside, look up, and see it. Right now itâs too faint to see without a telescope. But the good news is it appears to have been discovered about two weeks before it hits peak brightness. Supernovae get brighter over time before fading away, and this one may get as bright as 8th magnitude, which is within range of binoculars. Right now itâs at about 12th magnitude; the faintest star you can see with your naked eye is about mag 6 (note that the numbers run backwards; a bigger number is a fainter object).
M82 is in Ursa Major, well placed for viewing right now in the Northern Hemisphere. Universe Today has a map to show you how to find it.
Hereâs a funny thing, too. The supernova itself is what we call a Type Ia, a dwarf explosion. Astronomers are still trying to figure out exactly what happens in a Type Ia explosion, but there are three competing scenarios. Each involves a white dwarf, the small, dense, hot core left over after a star turns into a red giant, blows off its outer layers, and essentially âdies.â One scenario is that the white dwarf is orbiting a second star. It siphons off material from the star and accumulates it on its surface. Eventually this material gets so compressed by the huge gravity of the white dwarf that it fuses, creating a catastrophic explosion that tears the star apart.
Another is that two white dwarfs orbit each other. Eventually they spiral in, merge, and explode. The third, which is a recent idea, is that there are actually three stars in the system, a normal star and two white dwarfs. Due to the complex dance of gravity, the third star warps the orbits of the two dwarfs, and at some point they collide head-on! This too would result in a supernova explosion. All three scenarios involve very old stars, since it can take billions of years for a normal star to turn into a white dwarf.
Whatâs funny about this is that the galaxy M82 is undergoing a huge burst of star formation right now, and that means lots of massive stars are born. These live short lives and also explode as supernovae (called Type II, or core collapse) though the mechanism is very different from that of the white dwarf explosions. Youâd expect M82 to have more core collapse supernovae, but this new one is a Type Ia.
And thatâs actually more good news. These supernovae tend to all explode with the same energy, so they behave the same way whether they are near or far. We can see them for billions of light years away, which means they can be used to measure the distances of galaxies that are very far away. It was this kind of exploding star that allowed astronomers to discover dark energy, in fact. This energy is accelerating the expansion of the Universe, making it grow more every day. We donât know a whole lot about itâit was only announced in 1998âbut weâre learning more all the time. A nearby Type Ia means we can learn even more about these explosions, and hopefully calibrate our understanding even better.
And that means we need observations! If you are an amateur astronomer, get images! And if you observed M82 recently, you may have âpre-discoveryâ images of it, taken before it was officially discovered. Those are critical for understanding the behavior of the supernova. If you do, report it to the CBAT (but make sure you read the instructions first; they donât want images, just reports of magnitudes and so on).
Given the fact that itâs nearby, up high for so many observers, and caught so early, this may become one of the best-observed supernovae in modern times. Iâm very excited this happened, and I hope to share more images and information with you soon!
Lots of sites have more info. Here are a few:
Nicole Gugliucci at Cosmoquest
Sky and Telescope
Universe Today