Create a free profile to get unlimited access to exclusive videos, sweepstakes, and more!
Is This the Most Distant Object Ever Seen?

Well, this is pretty cool: A weird proto-galaxy spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope may have broken the record for the most distant object ever seen. Andâif it pans outâit didnât just break the record, it smashed it.
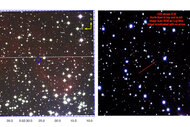
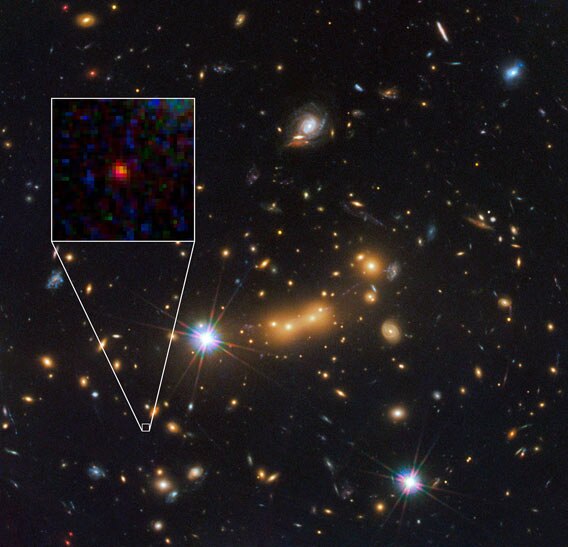
Hereâs the picture:
Yowza. [Click to redshiftenate, or grab the even bigger 1578 x 1520 version.]
The object in questionâcalled MACS0647-JDâis the red blob in the inset. If the calculations hold out, that gloppy looking thing may be at the mind-crushing distance of almost 13.3 billion light years. The light we see from it started on its way when the universe itself was only 420 million years old.
Just typing that made the hair on the back of my neck stand up.
So how does this work? What is this thing, and how did the scientists figure out how far away it is? OK, youâll have to bear with me. This takes a moment to explain, and itâs a bit of a mind flip, but itâs really cool.
Itâs Just a Shift to the Red
Youâve probably heard that the universe is expanding. When astronomers say that, what they mean is that space itself is expanding, carrying everything with it. I know thatâs a bit of a brain-twisty thing to think about, but go with it. We have a huge amount of evidence to support this idea, and essentially no professional astronomer seriously doubts it.
What this cosmic expansion means is that galaxies that are far away are moving away from us, and the farther away they are, the faster theyâre moving. Youâve probably also experienced the Doppler shift: Sounds change pitch if the source of the sound is moving toward or away from you. When a motorcycle passes you, it makes that familiar âEEEEeeeeeeeooooooowwwwwwww!â sound. The pitchâthe frequency of the soundâis higher as it approaches you, then drops when it passes.
A similar thing happens with light. An object moving toward you and emitting light will have the frequency of that light increase. When it moves away from you, the frequency drops. Frequency is related to color; the blue end of the spectrum has a higher frequency than the red end. So we say the light of something moving toward you is blue shifted, and red shifted if it moves away.
When we observe distant galaxies, we see this effect! The farther away a galaxy is, the more redshifted we see its light. In fact, thatâs how the universeâs expansion was first discovered. By measuring the amount of redshift we can tell how fast the galaxy is moving away from us and from that determine its distance.
Itâs not that easy, but thatâs the idea. Usually we use a spectrograph to get the color of the galaxy. This is a device that breaks the light up into thousands of individual colors, allowing a pretty precise determination of the redshift (Iâve done this sort of measurement myself, and it can yield amazingly accurate results). The problem is, something 13.3 billion light years away would be way too faint to see. Let alone measure. But in the case of MACS0647-JD, we had a little help from a few trillion friends.
Letâs Do the Space Warp Today
Take another look at the picture. Almost everything you see in it is a galaxy, a vast collection of hundreds of billions of stars. Theyâre part of a huge cluster of galaxies called MACS J0647.7 +7015. (I know, thatâs awful, but the nameâs from the Massive Cluster Survey, with its sky coordinates tacked on.) Now, are you ready for more brain-crushing weirdness? One of Albert Einsteinâs big ideas is that that mass literally bends space. The gravity of massive objects warps space, distorting it. Light moves through space and follows that warp, like a car driving along a curvy, hilly road.
The light from the distant galaxy MACS0647-JD had to pass through and around that galaxy cluster to reach us. The gravity of the cluster warps space, which acts like a lens, magnifying and brightening the light from the more distant galaxy! We actually call this effect gravitational lensing, and itâs (har har) massively useful, because it allows us to see distant objects that might otherwise be too faint to see. Such is the case here.
So yay, MACS0647-JD is now bright enough to see! Not only that, but due to the shape of the cluster, the light from the galaxy got split up and multiplied; We actually see three images of it in the big picture above. Iâve inset one here, just so you can see it.
But weâre still not done. Thereâs one more thing to know.
The Blackness Would Hit Me and the Void Would Be Calling
Even though it appears brighter than it normally would, MACS0647-JD is still way too faint to observe with a spectrograph to get its distance. Instead, astronomers did something clever. They used a series of filters to isolate various colors from the object, ranging from blue out to infrared. They even used observations from the orbiting Spitzer Space Telescope, which is designed to see ever farther out into the infrared. If this galaxy really is 13.3 billion light years away, then it must be an incredibly young object. Young galaxies are loaded with very hot, massive stars that blast out ultraviolet light, and in fact dominate the light emitted from such galaxies. If the galaxy is that far away, the expansion of the universe itself will redshift that UV light by a factor of nearly ten, pushing it well out into the infrared.
Sure enough, when they looked at the images from all the different filters, the galaxy is invisible in all but the infrared ones. Thatâs a pretty convincing sign it really is that far away. Iâll note the same team that found MACS0647-JD has used this same technique with other, somewhat closer objects, and those have been confirmed using spectroscopy. That lends credence to this new result.
So holy wow. This may really be a galaxy at that forbidding distance. Unfortunately, though, the research paper has not yet been published, so I havenât read it for myself. Still, the team involved is quite careful and almost certainly was meticulous in their analysis. I have little doubt their results are solid. There is still some chance this may be a foreground object masquerading as something more distant, but it seems unlikely.
So, to be fair, we have to say this is a candidate for the most distant object ever seen. And the funny thing is, itâs not terribly likely weâll find things much farther away! Thatâs because the farther away we look, the younger the universe was. And when it was only 420 million years old, it had barely gotten started. We might find things a few tens of millions of light years farther away, maybe even a hundred million or so. But the Universe started with a Big Bang 13.73 billion years ago, so thatâs a hard limit to how far away we can see.
And knowing its distance we can figure out how big MACS0647-JD is. It turns out to be pretty dinky as galaxies go: Itâs only about 600 light years across and has at most a billion stars. Compare that to our own Milky Way galaxy, living large at 100,000 light years across and containing 200â300 billion stars. MACS0647-JD really is a bit of a dim bulb. Itâs most likely still in the act of forming itself into a proper galaxy, so we call it a proto-galaxy. Our own galaxy formed from such modest beginnings as this.
But teeny or not, itâs still amazing. Weâre seeing it, quite literally, clear across the universe.
Finding objects like MACS0647-JD is critical to our understanding of the universe. They tell us what things were like when the universe was a mere whippersnapper, something thatâs very hard to do otherwise. We can learn how much gas was around back then, what stars were like, how galaxies formed, and even how great the effects of mysterious dark matter and dark energy were, about which very little is known. This new galaxy pushes the limits so hard that everything we learn from it is new.
Plus, itâs just so darn cool! Look at it again, it may just look like a lumpy red blob, but itâs telling us a vast amount about the entire universe we live in. Nothing lives in isolation, no scientific fact sits alone. Everything we see, everywhere, has an impact on what we understand. Even a tiny ball of stars 133 billion trillion kilometers away.